Definition and Simulation of Occupant Behaviour in Buildings
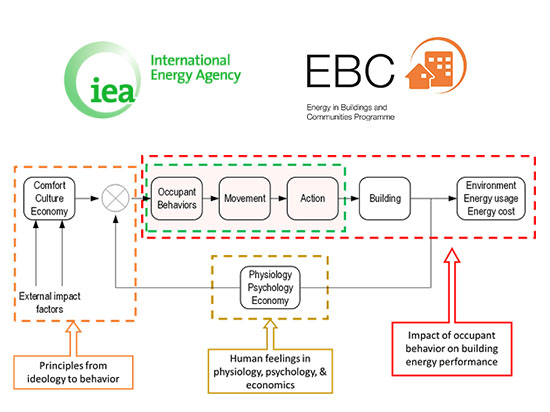
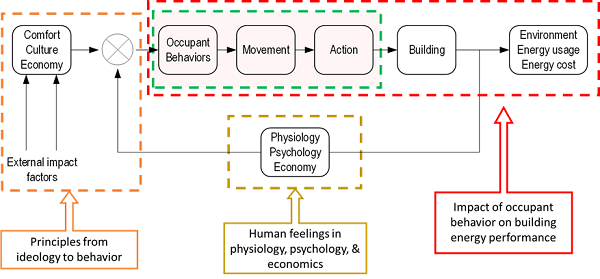
Energy related occupant behavior in buildings, for example adjusting thermostat for comfort, switching lights, opening/closing windows, pulling up/down window blinds, and moving between spaces, is a key issue for building design optimisation, energy diagnosis, performance evaluation, and building energy simulation due to its significant impact on real energy use and indoor environmental quality in buildings. However the influence of occupant behavior is under-recognized or over-simplified in the design, construction, operation, and retrofit of buildings.